Case of 24 Palm Corned Beef
PRAL or the potential renal acid load refers to the amount of acid produced when foods are digested. The higher the PRAL, the more acid produced. This also means more work for your kidney s. Those with poor kidney function should consider their PRAL food intake. Learn how different foods can help or hurt your kidneys depending on their PRAL value.
What is PRAL
PRAL stands for the potential renal acid load. In other words, this is the amount of acid that is produced by the body after digesting certain foods.
PRAL , Kidneys, and Acid Balance
Too much acid in the body can lead to metabolic disorders including insulin resistance, diabetes, heart disease, blood pressure, and other health conditions.
Excess body acid needs to be filtered and placed in the kidney's renal solute load. However, this is the name for all of the substances that are removed by the kidneys. Acid pushed out in a urinary excretion often referred to as the renal net acid excretion. It includes acid from both metabolic and dietary sources.
High PRAL Foods Can Affect Kidney Function
Animal proteins are a big source of acid. To clarify, these include meat, cheese, and eggs. Processed and sugary foods and beverages can also produce high amounts of acid.
Large consumption of these high PRAL foods produces a lot of acid. To prevent acidosis the kidneys will need to work harder to lower the body's pH and get rid of the excess acid. However, this can put a strain on the kidneys. Similarly, it may also lead to chronic kidney disease (CKD) and worsen existing kidney conditions.
The Potential of Hydrogen ( pH) Food Scale Determines PRAL
In case you're not familiar with pH here is a brief overview. Every substance has a potential of hydrogen or pH. In other words, this is a measure of how many hydrogen atoms are found in a specific substance.
So the ph food scale works the same way. It runs from 0 to 14. Seven is neutral and everything above seven is considered to be a base or alkaline. On the other hand, anything below seven is acid or acidic.
Compounds that contain a lot of hydrogens are acidic and have a pH of less than 7. Anything low in hydrogen atoms will be a base and have a ph greater than 7.
To give you an example, water is neutral at 7 a pH of seven while stomach acid is very acidic and has a pH of 2. Apples have a pH of 8 and celery has a pH of 9.
In other words, the lower the pH the more acidic the food.
This is the opposite of the PRAL value. Foods with a HIGH PRAL value will produce more acid.
But how do they assign value to these foods? With the PRAL value or Pral Score of a food.
What is PRAL Value or the PRAL Score of a Food
To find how acidic a food or diet was, the pH needs to be determined. This number became the PRAL value.
The PRAL values are based on a formula devised by Thomas Remer and other researchers at the Department of Nutrition and Health: The Research Institute of Child Nutrition, in Dortmund, Germany.
They found diets and certain food components had an impact on the body's acid-base balance. More importantly, they found the following parameters were necessary for estimating the PRAL value for food or diet:
- Protein, chloride, phosphorus, sodium, potassium, calcium, and magnesium content of a food
- How fast a nutrient is absorbed by the intestine
- The presence of the mineral sulfate made from certain amino acids
- How fast phosphorus from foods will be absorbed by the body at a pH of 7.4
- How quickly calcium can affect bond with magnesium
The total net acid excretion or PRAL score was determined by looking at all the substances that are produced when these foods are digested. However, it also takes into account the normal urine production versus the additional components that are produced from high acid foods.
How Do You Calculate PRAL Score
After looking at the effects of protein, phosphorus, potassium, and magnesium on the body, Remer and his colleagues came up with the following equation to assign a PRAL score to various foods and diets.
PRAL of a food =
0.49 x protein (gram/day)
+ 0.037 x phosphorus (mg/d)
— 0.021 x potassium (mg/day)
— 0.026 magnesium (mg/day)
— 0.013 x calcium (mg/day)
The results of this formula will give you a positive or negative PRAL value or score for any food.
- A POSITIVE score is an ACID-producing food
- A NEGATIVE score is a BASE or alkaline-producing food
How The PRAL Score Comes Out to Be a Negative or Positive Number
You may be wondering how a PRAL score becomes either a positive or negative number. That is to say, it has to do with the amount of the above nutrients found in each food.
If a food has a higher protein and phosphorus content it tends to result in a positive number. To clarify, this is because a larger number subtracted from a smaller results in a positive result. Therefore, foods high in protein and phosphorus will typically have a positive PRAL number.
If potassium, magnesium, and calcium totals are higher than protein and phosphorus levels that food will have a negative PRAL score. This is because a smaller number subtracted from a larger number equates to a negative number.
Examples of How PRAL Scores Result in Negative or Positive Numbers
Below are two examples of how both a negative and positive PRAL score is calculated.
Steak
Three ounces of a cooked steak will have a positive PRAL number of about 47. You can see how the protein and phosphorus numbers are higher than the calcium, potassium, and magnesium content of this food.
- Protein for PRAL = 0.49 x 95.5 g protein (PRO) = 46.795
- Phosphorus for PRAL = 0.037 x 197 mg phosphorus (PHOS) = 7.289
- Potassium for PRAL = 0.021 x 307 mg potassium (K) = 6.447
- Magnesium for PRAL = 0.026 x 22.2 mg magnesium (Mg) = 0.5772
- Calcium for PRAL 0.013 x 4.3 calcium mg (Ca) = 0.0559
PRAL of steak = 46.795 (PRO) + 7.289 (PHOS) – 6.447 (K) – 0.5772 (Mg) – 0.0559 (Ca)
PRAL of steak = 47.0039
Spinach
The PRAL of a cup of raw spinach will come out to about negative 2.9. This is because the spinach subtracts the smaller protein and phosphorus levels from the larger potassium, magnesium, and calcium content. Below is a breakout of how the higher potassium, magnesium, and calcium levels are what give spinach a lower PRAL score.
- Protein for PRAL = 0.49 x 2.1 g protein (PRO) = 1.029
- Phosphorus for PRAL = 0.037 x 14.7 mg phosphorus (PHOS) = 0.5439
- Potassium for PRAL = 0.021 x 167 mg potassium (K) = 3.507
- Magnesium for PRAL = 0.026 x 23.7 mg magnesium (Mg) = 0.6162
- Calcium for PRAL 0.013 x 29.7 calcium mg (Ca) = 0.3861
PRAL of spinach = 1.029 (PRO) + 0.5439 (PHOS) – 3.507 (K) – 0.6162 (Mg) – 0.3861(Ca)
PRAL of spinach = -2.9364
For anyone who hates math, you may be dreading having to compute the PRAL score formula but luckily you don't have to do anything. You can just look at the list below.
How PRAL Value Foods Differ From pH Levels
So Unlike pH, the higher the PRAL number, the more acid is produced from that food or diet. A negative PRAL value indicates that food will produce a base when consumed.
Metabolic Acidosis and Kidney Function
Balance is key when it comes to acid levels in the body. However, too much can be bad for health. Firstly, acid is naturally produced from metabolic processes like respiration and digestion. The lungs and kidneys are responsible for making sure body pH or acid levels don't get too high.
Diets high in PRAL foods can also lead to high acid production. A study in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition indicated that protein intake leads to high acid levels in those with poor kidney function. This is because they will have trouble clearing acid from the body and it will accumulate in the blood. Subsequently, high levels of acid lead to metabolic acidosis.
Metabolic acidosis in CKD is common. It can affect about 15 to 19% of patients. Risk also increases with age.
However, one way to look out for acidosis is to keep track of your acid levels. This is done by having your doctor monitor the carbon dioxide in your blood.
Serum bicarbonate is the lab used to check for acidosis. Normal levels are 22 to 29 mEq/L. Metabolic acidosis occurs when bicarbonate levels drop under 22 mEq/L.
Metabolic Acidosis can lead to the following health problems:
- Increased bone loss (osteoporosis)
- Muscle loss
- High blood sugar
- Death
Moreover, signs and symptoms of metabolic acidosis include the following:
- Long and deep breaths
- Fast heartbeat
- Headache
- Confusion
- Weakness
- Fatigue
- Nausea and vomiting
- Loss of appetite
Similarly, those with kidney dysfunction and metabolic acidosis are also at risk for developing kidney disease. Read more about the renal function panel here.
High Acid to Alkaline Diet: A Treatment for Acidosis
Acidosis is a very serious and scary condition. But there is something you can do to treat it. Some research indicates taking sodium bicarbonate (baking soda) or sodium citrate pills will help increase the levels of the base in your body.
The idea behind using baking soda and alkali supplements is that they will fill your body with base. More base will neutralize the excess acid. It should also protect your kidneys from further wear and tear. To note, this treatment is not recommended unless your healthcare professionals give you the go-ahead to try it out yourself.
It's important to know that self-treating with baking soda may cause other problems. Just one teaspoon of baking soda has 1,259 milligrams of sodium – more than half a day's worth. Sodium bicarbonate tabs, though, have just 178 milligrams sodium per tablet.
However, an easier way to lower the risk for metabolic acidosis would be to just start incorporating more alkaline foods into the diet.
Low PRAL and Foods on the Alkaline Diet
As we discussed earlier, the lower the PRAL value the less acid produced. Foods on the alkaline diet produce base when digested by the body. This leads to a lower pH and alkaline environment. Simply, the more alkaline your diet the lower your acid levels. So implementing an alkaline diet can lead to less pressure on the kidneys.
Low PRAL alkalinity-promoting foods include fruits and vegetables. Similarly, these foods are higher in potassium, magnesium, and calcium. These nutrients are what help the body produce more bicarbonate or base.
PRAL Alkaline Foods vs. Acidic foods
You may be thinking, "wait for a second! Lemon is an acidic food, will this cause me to produce acid?" That answer is no. To clarify, acidic foods are different from alkaline foods.
There are foods with a low pH. Therefore, the acid produced by the body from high PRAL foods should not be confused with foods that have a low pH.
Acidic foods can be tolerated by the body because they are neutralized by the hydrochloric acid in the stomach during digestion. Therefore, foods like lemons and tomatoes can be both acidic and alkaline at the same time.
Foods with a higher pH (bases) can also be a high PRAL food. For example, red meat, cheese, has a pH of around 5 or 6.
To get a better idea of how foods impact PRAL look at this acid-alkaline chart.
PRAL Acid-Alkaline Chart
The PRAL acid-alkaline chart breaks down foods by how much acid and base (alkaline) they produce. The lower the number the more base there is. Therefore, you want to look for low and negative numbered PRAL foods to include in your diet.
PRAL Acid Foods
Below is a list of acid-producing foods measured in milliequivalents of acid per day (mEq/day).
| Food | Food Group | PRAL Value (mEq/day) |
|---|---|---|
| Low-fat vanilla yogurt | Dairy and Egg | 0.1727 |
| Whipped cream | Dairy and Egg | 0.175 |
| Low-fat milk (1% fat) | Dairy and Egg | 0.1833 |
| Whole milk (3.25% fat) | Dairy and Egg | 0.2128 |
| Instant oatmeal (apple | Cereals Grains and Pasta | 0.2338 |
| Beef gravy soups | Sauces and Gravies | 0.2861 |
| Whipped salted butter | Dairy and Egg | 0.3575 |
| Saccharin | Sweets | 0.3766 |
| Chocolate fudge with nuts | Sweets | 0.3782 |
| Fat-free sour cream | Dairy and Egg | 0.44 |
| Vanilla ice cream | Sweets | 0.496 |
| Mayonnaise | Fats and Oils | 0.514 |
| English muffins | Baked | 0.566 |
| Soy milk | Legumes | 0.576 |
| Bulgur | Cereal Grains and Pasta | 0.5992 |
| Tortilla chips | Snacks | 0.6441 |
| Chocolate Wafer Bar | Sweets | 0.7469 |
| Banana bread | Baked | 0.802 |
| Pork and chicken lunch meat | Sausages & Lunch Meats | 0.8397 |
| White rice | Cereal Grains and Pasta | 0.9198 |
| Rice noodles | Cereal Grains and Pasta | 0.9719 |
| Buckwheat groats | Cereal Grains and Pasta | 0.9812 |
| Frozen Cheese lasagna | Meals, Entrees, & side dishes | 1.6573 |
| Raisin bread | Baked | 1.75 |
| Whole wheat bread | Baked | 1.906 |
| Oysters | Finfish & Shellfish | 1.9648 |
| Oat bran | Cereal Grains and Pasta | 2.8739 |
| Buttermilk pancakes | Baked | 2.999 |
| Peanut butter | Legumes | 3.2024 |
| Tofu | Legumes | 3.4531 |
| Cream cheese | Dairy and Egg | 3.8525 |
| Pork | Pork | 3.9957 |
| Frozen turkey and gravy | Poultry | 4.2072 |
| Lamb | Lamb, Veal, and Game | 4.4118 |
| Pork & turkey sausage | Sausages & Lunch Meats | 4.4945 |
| Croissants | Baked | 4.528 |
| Brown gravy | Sauces and Gravies | 4.6716 |
| Pork patties | Pork | 4.753 |
| Granola Breakfast bars, | Snacks | 4.799 |
| Corned beef | Beef | 4.8302 |
| No salt oil roasted mixed nuts | Nuts | 4.8898 |
| Veal | Lamb, Veal, and Game | 4.9628 |
| Mackerel | Finfish and shellfish | 5.125 |
| Anchovy | Finfish and shellfish | 5.3895 |
| Frozen cheese pizza | Fast Foods | 5.5824 |
| Pacific herring | Finfish and shellfish | 5.6731 |
| Low salt wheat crackers | Baked | 5.842 |
| Whole milk ricotta cheese | Dairy and Egg | 6.1814 |
| Halibut | Finfish and shellfish | 6.1919 |
| Salted cashews | Nuts | 6.4219 |
| Cod | Finfish and shellfish | 6.5249 |
| Ham | Sausages & Lunch Meats | 6.614 |
| Macaroni | Cereal Grains and Pasta | 6.9256 |
| White rice | Cereal Grains and Pasta | 6.9808 |
| Turkey breast | Sausages & Lunch Meats | 7.3663 |
| Lobster | Finfish and shellfish | 7.439 |
| Couscous | Cereal Grains and Pasta | 7.6004 |
| Brazil nuts, unblanched | Nuts | 8.1468 |
| Blue crab | Finfish and shellfish | 8.3724 |
| Atlantic mackerel | Finfish and shellfish | 8.417 |
| Pine nuts | Nuts | 8.7121 |
| Oven-roasted chicken breast (fat-free) | Sausages & Lunch Meats | 8.7281 |
| Raw tuna | Finfish and shellfish | 9.186 |
| Wild rice | Cereal Grains and Pasta | 9.3967 |
| Egg, whole | Dairy and Egg | 9.4162 |
| Pastrami (98% fat-free) | Sausages & Lunch Meats | 9.781 |
| Beef ribs | Beef | 9.8355 |
| Roasted turkey | Poultry | 10.491 |
| Brie cheese | Dairy and Egg | 11.0195 |
| Atlantic salmon | Finfish and shellfish | 11.114 |
| Rye | Cereal Grains and Pasta | 11.9514 |
| Durum wheat | Cereal Grains and Pasta | 12.2622 |
| Ground pork | Pork | 12.4381 |
| Ground beef, (90% lean) | Beef | 12.5339 |
| Veal | Lamb, Veal, and Game | 12.6367 |
| Light canned tuna no salt | Finfish and shellfish | 12.7089 |
| Camembert cheese | Dairy and Egg | 13.05 |
| Roasted chicken | Poultry | 13.8479 |
| Mozzarella cheese (part-skim milk) | Dairy and Egg | 16.4904 |
| Low-calorie lemonade (aspartame) | Beverages | 18.393 |
| Swiss cheese | Dairy and Egg | 21.2867 |
| Reduced calorie (aspartame) | Sweets | 74.592 |
| Pudding | Sweets | 85.3939 |
| Baking phosphate | Baked | 270.164 |
Acid-Producing Foods Do Not Need to be Avoided
Rather, think of this as a balancing act. When adding foods mentioned above, it will be beneficial to balance them with alkaline foods listed below.
For example, -10 + 4 = -6. There is still a "positive" value in this equation, however the end result is still negative.
PRAL Neutral Foods
Below is a list of neutral foods measured in milliequivalents of acid per day (mEq/day).
| Food | Serving Size | Food Group | PRAL Value |
| Cod liver fish oil | 1 tbsp | Fats and OIls | 0 |
PRAL Alkaline Foods
Below is a list of alkaline foods measured in milliequivalents of acid per day (mEq/day).
| Food | Food Group | PRAL Value |
|---|---|---|
| Parsley | Vegetables | -108.647 |
| Coriander | Spices and Herbs | -99.4853 |
| Chervil | Spices and Herbs | -92.4 |
| Basil | Spices and Herbs | -85.3627 |
| Celery flakes | Vegetables | -84.464 |
| Dried parsley | Spices and Herbs | -81.4902 |
| Dried Oriental radishes | Vegetables | -74.552 |
| Dill weed | Spices and Herbs | -74.5146 |
| Tarragon | Spices and Herbs | -64.5107 |
| Chives | Vegetables | -59.815 |
| Tomatoes | Vegetables | -58.3551 |
| Dried spearmint | Spices and Herbs | -55.4223 |
| Sweet green peppers | Vegetables | -52.33 |
| Sweet red peppers | Vegetables | -52.33 |
| Oregano | Spices and Herbs | -49.767 |
| Marjoram | Spices and Herbs | -49.3026 |
| Seaweed | Vegetables | -46.8031 |
| Turmeric | Spices and Herbs | -46.6693 |
| Leeks | Vegetables | -39.016 |
| Molasses | Sweets | -38.554 |
| Rosemary | Spices and Herbs | -37.4338 |
| Paprika | Spices and Herbs | -36.3376 |
| Thyme | Spices and Herbs | -35.4831 |
| Pasilla peppers | Vegetables | -35.3725 |
| Fennel | Spices and Herbs | -35.371 |
| Celery | Spices and Herbs | -34.7177 |
| Dill seed | Spices and Herbs | -33.1908 |
| Apricots dehydrated | Fruits & Fruit Juices | -33.071 |
| Cumin | Spices and Herbs | -31.9771 |
| Cloves | Spices and Herbs | -31.5888 |
| Bananas | Fruits & Fruit Juices | -29.7609 |
| Black pepper | Spices and Herbs | -25.3975 |
| Ginger | Spices and Herbs | -24.5502 |
| Cinnamon | Spices and Herbs | -23.7569 |
| Coriander seed | Spices and Herbs | -23.2097 |
| Shallots | Vegetables | -22.754 |
| Cardamom | Spices and Herbs | -22.5736 |
| Shiitake mushrooms | Vegetables | -20.2168 |
| Beet greens (cooked) | Vegetables | -19.5627 |
| Lima beans | Legumes | -18.3206 |
| Aniseed | Spices and Herbs | -18.175 |
| Carob flour | Legumes | -18.1082 |
| Canned tomato paste | Vegetables | -17.6662 |
| Bay leaf Spices and Herbs | Spices and Herbs | -17.1611 |
| Beet greens (raw) | Vegetables | -16.748 |
| Fresh Rosemary | Spices and Herbs | -16.4511 |
| Dried Litchis | Fruits & Fruit Juices | -16.272 |
| Dried Peaches | Fruits & Fruit Juices | -16.2001 |
| Dried peeled chestnuts | Nuts | -16.0431 |
| Thyme | Spices and Herbs | -15.5676 |
| Dill weed | Spices and Herbs | -15.4946 |
| Yams | Vegetables | -15.1183 |
| French beans | Legumes | -14.4771 |
| Raisins | Fruits & Fruit Juices | -14.4592 |
| Roasted pumpkin seeds | Nuts | -14.3325 |
| Dried persimmons | Fruits & Fruit Juices | -14.2998 |
| Dried currants | Fruits & Fruit Juices | -14.2918 |
| Dried figs | Fruits & Fruit Juices | -14.058 |
| Dried unpeeled Chestnuts | Nuts | -13.8949 |
| Medjool dates | Fruits & Fruit Juices | -13.6711 |
| Black beans | Legumes | -13.58 |
| Lemon grass (citronella) | Vegetables | -12.9592 |
| Peppermint | Spices and Herbs | -12.6495 |
| Taro root | Vegetables | -12.5929 |
| White beans | Legumes | -12.5801 |
| Pine nuts | Nuts | -12.4117 |
| Swiss chard | Vegetables | -12.3768 |
| Boiled chestnuts | Nuts | -12.374 |
| Fermented tofu | Legumes | -12.3655 |
| Deglet dates | Fruits & Fruit Juices | -11.9065 |
| Spinach | Vegetables | -11.8446 |
| Dehydrated apples | Fruits & Fruit Juices | -11.5772 |
| Pink beans | Legumes | -11.5406 |
| Parsley | Spices and Herbs | -11.1267 |
| Kidney beans | Legumes | -11.0587 |
| Black bean soup | Legumes | -11.0475 |
| Kale | Vegetables | -10.737 |
| Purslane | Vegetables | -10.722 |
| Mustard spinach | Vegetables | -10.331 |
| Cooked spinach | Vegetables | -10.2887 |
| Banana chips | Snacks | -10.267 |
| Dried Chinese chestnuts | Nuts | -10.1082 |
| Wasabi | Vegetables | -10.074 |
| Basil | Spices and Herbs | -10.0124 |
| Spearmint (fresh) | Spices and Herbs | -10.0109 |
| Water chestnuts | Vegetables | -9.962 |
| Bamboo shoots (cooked) | Vegetables | -9.9373 |
| Cilantro (coriander) | Vegetables | -9.6683 |
| Pinto beans | Legumes | -9.5952 |
| Raw plantains | Fruits & Fruit Juices | -9.585 |
| Hyacinth beans | Legumes | -9.508 |
| Dried pears | Fruits & Fruit Juices | -9.3937 |
| Cooked plantains | Fruits & Fruit Juices | -9.1999 |
| Northern beans | Legumes | -9.0656 |
| Pinto beans | Vegetables | -9.059 |
| Peaches (dehydrated) | Fruits & Fruit Juices | -9.0131 |
| Grapefruit juice | Fruits & Fruit Juices | -8.7247 |
| Winter squash, | Vegetables | -8.6619 |
| Russet potatoes | Vegetables | -8.6483 |
| Cranberry beans | Legumes | -8.6303 |
| Avocados | Fruits & Fruit Juices | -8.6116 |
| Cowpeas | Vegetables | -8.6085 |
| Kidney beans | Legumes | -8.4118 |
| Horseradish | Vegetables | -8.362 |
| Kale | Vegetables | -8.337 |
| Chicory greens | Vegetables | -8.328 |
| Sweet potato | Vegetables | -8.1881 |
| Apples (dried) | Fruits & Fruit Juices | -8.1863 |
| Swiss chard | Vegetables | -8.144 |
| Bamboo shoots (raw) | Vegetables | -7.983 |
| Dandelion greens | Vegetables | -7.939 |
| Ginger root | Vegetables | -7.8912 |
| Arugula | Vegetables | -7.8628 |
| Chinese cabbage | Vegetables | -7.4486 |
| Fennel | Vegetables | -7.3154 |
| Turnip greens (raw) | Vegetables | -7.203 |
| Bananas | Fruits & Fruit Juices | -6.9369 |
| Guavas | Fruits & Fruit Juices | -6.8335 |
| Agar (seaweed) | Vegetables | -6.7404 |
| Mustard greens | Vegetables | -6.691 |
| Adzuki beans | Legumes | -6.6607 |
| Kale | Vegetables | -6.615 |
| Rhubarb | Fruits & Fruit Juices | -6.519 |
| Collards frozen uncooked | Vegetables | -6.3629 |
| Collards cooked | Vegetables | -6.3267 |
| Prickly pears | Fruits & Fruit Juices | -6.3123 |
| Kiwifruit | Fruits & Fruit Juices | -6.1249 |
| Dried figs | Fruits & Fruit Juices | -6.0692 |
| Endive | Vegetables | -6.0115 |
| Zucchini | Vegetables | -6.0011 |
| Parsnips | Vegetables | -5.882 |
| Jerusalem artichokes | Vegetables | -5.767 |
| Roasted salted soybeans | Legumes | -5.7452 |
| Parsnips | Vegetables | -5.7422 |
| Carrots | Vegetables | -5.7103 |
| Watercress | Vegetables | -5.689 |
| Passion-fruit juice | Fruits & Fruit Juices | -5.6599 |
| White beans | Legumes | -5.6403 |
| Kiwi fruit | Fruits & Fruit Juices | -5.6194 |
| Pumpkin | Vegetables | -5.607 |
| Okra | Vegetables | -5.587 |
| Guavas | Fruits & Fruit Juices | -5.5638 |
| Papayas | Fruits & Fruit Juices | -5.4851 |
| Beets (raw) | Vegetables | -5.3621 |
| Burdock root | Vegetables | -5.3523 |
| Green hot chili peppers | Vegetables | -5.342 |
| Currants | Fruits & Fruit Juices | -5.232 |
| Oriental radishes (cooked) | Vegetables | -5.2237 |
| Chinese broccoli (cooked) | Vegetables | -5.1734 |
| Yellow snap beans | Vegetables | -5.1579 |
| Crushed canned tomatoes | Vegetables | -5.1274 |
| Coconut water | Nuts | -5.1192 |
| Brussel sprouts | Vegetables | -5.1038 |
| Prune juice | Fruits & Fruit Juices | -5.0921 |
| Passion fruit juice | Fruits & Fruit Juices | -5.0787 |
| Cantaloupe melon | Fruits & Fruit Juices | -5.0694 |
| Chinese cabbage (raw) | Vegetables | -5.047 |
| Celery, raw Vegetables | Vegetables | -5.0399 |
| Red hot chili peppers | Vegetables | -5.0347 |
| Scallions | Vegetables | -4.9863 |
| Turnip greens (cooked) | Vegetables | -4.9844 |
| Beets (cooked) | Vegetables | -4.9818 |
| Globe or french Artichokes | Vegetables | -4.9697 |
| White radishes | Vegetables | -4.89 |
| Mustard cabbage | Vegetables | -4.889 |
| White beans | Legumes | -4.8846 |
| Figs (raw) | Fruits & Fruit Juices | -4.8835 |
| Horseradish | Spices and Herbs | -4.8708 |
| Kelp | Vegetables | -4.8218 |
| Pomegranates | Fruits & Fruit Juices | -4.7945 |
| Canned carrot juice | Vegetables | -4.7885 |
| Chives | Vegetables | -4.7557 |
| Radicchio | Vegetables | -4.7463 |
| Elderberries | Fruits & Fruit Juices | -4.7376 |
| Cabbage | Vegetables | -4.7231 |
| Chinese cabbage (raw) | Vegetables | -4.676 |
| Green onions | Vegetables | -4.67 |
| Canned tomatoes wedges | Vegetables | -4.6569 |
| Passion-fruit | Fruits & Fruit Juices | -4.624 |
| Cabbage | Vegetables | -4.6104 |
| Shallots | Vegetables | -4.596 |
| Broccoli raab | Vegetables | -4.5283 |
| Portabella mushrooms | Vegetables | -4.519 |
| Honeydew melon | Fruits & Fruit Juices | -4.4544 |
| Cauliflower | Vegetables | -4.4408 |
| Longans | Fruits & Fruit Juices | -4.4401 |
| Apricots (raw) | Fruits & Fruit Juices | -4.331 |
| Tomatillos (raw) | Vegetables | -4.3256 |
| Lemon peel | Fruits & Fruit Juices | -4.313 |
| Baby carrots | Vegetables | -4.3034 |
| Red cabbage | Vegetables | -4.2933 |
| Crimini mushrooms | Vegetables | -4.211 |
| Broccoli | Vegetables | -4.1968 |
| Collards | Vegetables | -4.0975 |
| Yellow raw tomatoes | Vegetables | -4.0608 |
| Toasted coconut meat | Nuts | -3.973 |
| Broccoli | Vegetables | -3.9692 |
| Orange with peel | Fruits & Fruit Juices | -3.939 |
| Cherries (sweet) | Fruits & Fruit Juices | -3.8206 |
| Nutmeg | Spices and Herbs | -3.7574 |
| Quinces | Fruits & Fruit Juices | -3.663 |
| Orange juice | Fruits & Fruit Juices | -3.657 |
| Kumquats | Fruits & Fruit Juices | -3.6078 |
| Oranges | Fruits & Fruit Juices | -3.581 |
| Cauliflower | Vegetables | -3.5095 |
| Tangerines | Fruits & Fruit Juices | -3.1421 |
| Green leaf lettuce | Vegetables | -3.1406 |
| Peaches | Fruits & Fruit Juices | -3.1161 |
| West Indian cherry | Fruits & Fruit Juices | -3.087 |
| Nectarines | Fruits & Fruit Juices | -3.0516 |
| Cherries (sour) | Fruits & Fruit Juices | -3.03 |
| Mangos | Fruits & Fruit Juices | -2.9831 |
| Red leaf lettuce | Vegetables | -2.9803 |
| Strawberries (frozen) | Fruits & Fruit Juices | -2.9103 |
| Blackberries | Fruits & Fruit Juices | -2.8039 |
| Coconut meat | Nuts | -2.6773 |
| Garlic | Vegetables | -2.6466 |
| Plums | Fruits & Fruit Juices | -2.622 |
| Strawberries (fresh) | Fruits & Fruit Juices | -2.5427 |
| Cucumber | Vegetables | -2.4265 |
| Raspberries | Fruits & Fruit Juices | -2.407 |
| Celery root | Vegetables | -2.389 |
| Litchis | Fruits & Fruit Juices | -2.3623 |
| Pineapple | Fruits & Fruit Juices | -2.3354 |
| Pinto beans | Vegetables | -2.3335 |
| Pears | Fruits & Fruit Juices | -2.2048 |
| Asparagus | Vegetables | -2.193 |
| Lime juice | Fruits & Fruit Juices | -2.1232 |
| Apples (raw) | Fruits & Fruit Juices | -1.9206 |
| Wakame seaweed | Vegetables | -1.3373 |
| Blueberries | Fruits & Fruit Juices | -1.0444 |
| Goat milk | Dairy and Egg | -0.5386 |
| Macadamia | Nuts | -0.4579 |
| Cranberries | Fruits & Fruit Juices | -1.3729 |
| Tapioca | Cereal Grains and Pasta | -0.1649 |
| Quinoa | Cereal Grains and Pasta | -0.191 |
| Chamomile tea | Beverages | -0.241 |
| Tofu yogurt | Legumes | -0.44 |
PRAL Food Groups to Make Eating Easier
Having to check the individual foods may be quite timely. However, to make it easier, we are also providing you with food groups that have different effects on acid production. Below are various food groups that will increase, decrease, and moderately elevate PRAL.
Food Groups That Increase PRAL (Acid Producing Foods)
Firstly, food groups that increase PRAL include:
- Beef
- Sweets
- Pork
- Poultry
- Lamb, veal, and game
- Baked items
- Some nuts
- Alcohol and beer
Food Groups That Moderately Elevate PRAL
Secondly, food groups that moderately elevate PRAL include the following:
- Cereals grains and pasta
- Eggs and dairy
- Some fats and oil
- Baked items
- Finfish and shellfish
Food Groups that Lower PRAL (Base Producing Foods)
Lastly, foods groups that lower PRAL are:
- Vegetables
- Fruits
- Beans and legumes
- Some nuts
Low PRAL Renal Diet Guidelines
Picking out individual PRAL food and foods groups may be time-consuming. However, an easier way to decrease your acid levels is by following these renal diet guidelines.
Increase your consumption of fruits and vegetables that are good for kidney health. The key to lowering your acid production will be to eat more foods that make base. Therefore, tating a large number of fruits and vegetables is an easy way to ensure this.
Change the types of protein you consume. As you can see protein foods produce a high PRAL value. This means more acid. The more acid in your diet, the harder your kidneys will be working. So swap out some animal proteins for lower PRAL plant proteins.
Limit your servings of high PRAL proteins. Animal protein foods can do to a number on your kidneys. Even just reducing protein portion sizes can lower the amount of acid that is being produced. A good rule of thumb is having about 3 oz. Or look at the portion in relation to the size of your palm. If it's bigger than your hand then you should scale back on the size.
PRAL Diet Comparisons
If you are feeling overwhelmed by having to pick out low PRAL foods here are some diets you can try to ensure you are getting enough low PRAL foods.
Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension DASH Diet
The Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension or DASH diet was designed to help lower blood pressure. It is a heart-healthy low sodium diet with a lot of low PRAL fruits, vegetables, and plant proteins. It also recommends whole grains and healthy fats. High PRAL animal proteins and saturated fats are allowed in moderation. Nuts, seeds, beans, peas, and sweets are also limited to specific servings during the week. See the serving breakout below:
- Grains: 6 – 8 servings per day
- Meats, poultry, and fish: 6 or fewer servings per day
- Vegetables: 4 – 5 servings per day
- Fruit: 4 – 5 servings per day
- Low-fat or fat-free dairy products: 2–3 servings per day
- Fats and oils: 2 – 3 servings per day
- Sodium: 1,500 – 2,300 mg per day
- Nuts, seeds, dry beans, and peas: 4–5 servings per week
- Sweets: 5 or fewer servings per week
The Mediterranean Diet
The Mediterranean Diet is another meal plan offering a lot of low PRAL foods. This eating plan has been devised to help improve heart health, diabetes, and brain function.
It is based on the regular consumption of olive oil as a main source of fat. It incorporates a lot of whole grains, fruits, vegetables, legumes, tree nuts, and seeds.
Animal proteins, fish, seafood, and dairy are allowed in moderation. Red meat and other meat products are limited to about two times a week.
PRAL Considerations for Kidney Disease
Though a diet high in fruits and vegetables can improve health, those with kidney conditions like CKD need to be mindful of certain nutrients in their diet. If you need to restrict potassium, phosphorus, and other electrolytes, be sure to limit your intake of foods containing these nutrients.
Alkaline Supplements vs Low PRAL Foods
Like with all health conditions there are many products on the market offering a quick fix to lower acid levels. Don't be fooled by these marketing tactics. There is little research indicating these products can work. Worse yet they may even cause harm.
One popular product is alkaline water. This drink contains a large amount of base. Just like when there is too much acid, an excess in base in the blood can result in alkalosis. Alkalosis is when the body's pH becomes elevated. Signs of alkalosis include:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Hand tremors
- Muscle twitching
- Tingling in the extremities
- Face confusion
- Decrease calcium
The best way to avoid acidosis or alkalosis is by having a varied diet of low PRAL foods. If you do find an alkaline product you are interested in it is best to talk to your doctor before trying it.
Summary
As discussed, the potential renal acid load or PRAL value is a number calculated by how nutrients in food metabolize into acid in the blood. The higher the PRAL value the more acid that is produced. Therefore, eating a diet full of high PRAL foods can put you at risk for metabolic acidosis. Consequently, this condition can lead to many metabolic disorders including insulin resistance, diabetes, heart disease, and high blood pressure.
The kidneys work to clear acid production but those with kidney dysfunction will have a harder time getting rid of acid in the blood. Therefore, there is a higher risk for metabolic acidosis with kidney issues. Following a low PRAL diet can prevent acid build-up and preserve kidney function. Eating foods that produce more base such as fruits and veggies, swapping out animal proteins for low PRAL plant proteins, and eating smaller servings of animal protein can also help kidney function.
Supplements and medications recommended for increasing the alkalinity in the blood can be tempting to try but caution should be taken with these as they may cause more harm than good. It is best to talk to your doctor before taking any low PRAL supplements.
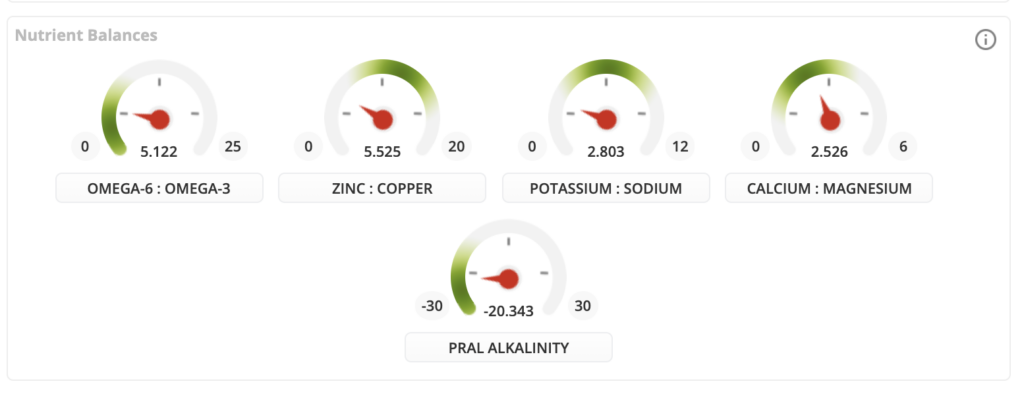
Want to see how your PRAL your diet is?
Interested in seeing where your diet falls in the PRAL values? I highly recommend you check out Cronometer Pro. The Cronomteter Gold membership (only $40 per year!) can tell you your daily PRAL values based on your logged meals. And I've got a special discount code for you start tracking today!
*This is an affiliate link in which I receive a very small commission, at no expense to you. Thank you for your support!
willinghamjoods1973.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.plantpoweredkidneys.com/pral/
0 Response to "Case of 24 Palm Corned Beef"
Post a Comment